When working on a Cummins diesel engine, knowing the correct torque specifications is crucial for ensuring proper assembly, performance, and longevity. Whether you’re rebuilding an engine, replacing components, or performing routine maintenance, adhering to the correct torque settings is essential to avoid damage and ensure reliability.
Below, you’ll find detailed torque specifications for various Cummins engine models, covering critical components such as cylinder head bolts, main bearing caps, connecting rods, rocker arms, flywheel bolts, and more.
Cummins Engine Torque Specifications by Model
Cummins 6B, 6BT, and 6BTA 5.9L Torque Specs

The Cummins 6BT 5.9 engine is one of the most popular and reliable diesel engines, widely used in marine, industrial, and truck applications. Proper torque settings are essential to maintaining its durability. Key torque specs include cylinder head bolts, which require a precise multi-step tightening sequence to ensure even clamping pressure, and main bearing caps, which must be torqued correctly to prevent crankshaft misalignment.
Torque Specs For Cummins 6B, 6BT, 6BTA 5.9L Marine & Industrial Engines
Cummins 4BT Torque Specs

The Cummins 4BT is a compact yet powerful diesel engine used in industrial and marine applications. Correct torque values for head bolts and rocker arms are critical to maintaining its longevity. The turbocharger mounting bolts also require precise torquing to prevent exhaust leaks and maintain boost efficiency.
Torque Specs For Cummins 4B, 4BT, 4BTA 3.9L Marine & Industrial Engines
Cummins 6C, 6CT, and 6CTA 8.3 Torque Specs

The Cummins 6CTA 8.3 is a robust mid-range engine used in marine and industrial applications. Proper torque values for this engine are critical, especially for components like the connecting rods and rocker arms, which experience significant stress under load. Flywheel bolts also require precise torque settings to prevent vibration and excessive wear over time.
Torque Specs For Cummins 6CTA 8.3 Marine Engines
Cummins QSB 6.7L Torque Specs

The QSB 6.7 is an advanced version of the 6.7L Cummins engine, featuring electronic fuel control for improved efficiency. Torque specs for this engine are crucial for high-performance applications, especially in marine and heavy-duty machinery. Cylinder head bolts require a multi-stage torque sequence, while main bearing caps must be torqued evenly to prevent bottom-end failures.
Torque Specs For Cummins QSB Marine & Industrial Engines
Cummins QSC 8.3L Torque Specs
The Cummins QSC 8.3 is a popular choice for marine and industrial applications, offering electronic fuel injection and improved emissions compliance. This engine shares a base with the 6CTA 8.3, but proper torque specs are essential for its electronically controlled components. Key areas requiring precision include injector hold-down bolts, cylinder head bolts, and main bearing caps, ensuring proper fuel delivery and combustion efficiency.
Torque Specs For Cummins QSC 8.3L Marine & Industrial Engines
Cummins ISC 8.3 Torque Specs
The Cummins ISC 8.3 is another evolution of the 8.3L engine, commonly used in commercial and industrial applications. Proper torque values are necessary to maintain engine balance and prevent excessive wear. Cylinder head bolts require a precise tightening sequence to prevent warping, and the rocker arm assembly must be torqued correctly to maintain accurate valve timing.
Torque Specs For Cummins ISC 8.3L Marine & Industrial Engines
Cummins ISL 8.9L Torque Specs
The Cummins ISL 8.9 is a high-performance engine found in buses, trucks, and marine applications. Proper torque specs are vital for maintaining its high durability. The main bearing caps and connecting rod bolts must be tightened according to precise specifications to handle the high compression and stress of this engine. Additionally, flywheel bolts must be torqued correctly to prevent drivetrain vibrations.
Torque Specs For Cummins ISC 8.3L Marine & Industrial Engines
Cummins ISX Torque Specs
The Cummins ISX is known for its high power output and fuel efficiency. Torque specs play a critical role in preventing premature wear and maintaining emissions compliance. Cylinder head bolts require precise torque application due to the engine’s high compression, while injector hold-down bolts must be torqued properly to avoid fuel system leaks.
Cummins KTA 19 Torque Specs

The Cummins KTA 19 is a high-horsepower engine used in large marine, industrial, and power generation applications. Given its size and power output, precise torque settings are crucial for ensuring reliability. Cylinder head bolts must be torqued in a specific sequence to prevent warping, while connecting rod bolts require exact torque values to handle the extreme forces at high RPMs.
Torque Specs For Cummins KTA19 Marine & Industrial Engines
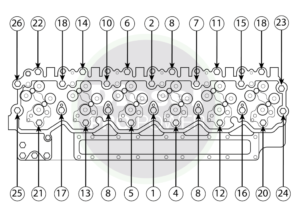
Cummins N14 Torque Specs
The Cummins N14 is a workhorse in heavy-duty trucking and industrial applications. Proper torque settings help prevent premature wear and ensure peak performance. The rocker arm assemblies and cylinder head bolts require exact torquing to maintain proper valve timing and prevent leaks, while main bearing caps need consistent torque values to support the crankshaft’s movement.
Cummins 855 Torque Specs
The Cummins 855 is a legacy engine known for its durability in heavy-duty trucking and industrial applications. Proper torque specs are essential, particularly for cylinder head bolts, which must be torqued in a specific sequence to prevent gasket failure. Flywheel bolts must also be torqued correctly to avoid vibration and engine imbalance.
Why Torque Specs Matter

Proper torque specifications are essential for maintaining the structural integrity, performance, and longevity of a Cummins diesel engine. Each bolt and fastener in an engine plays a crucial role in securing critical components, and improper torque application can lead to severe mechanical failures, increased downtime, and costly repairs.
1. Prevents Bolt Over-Tightening
Over-tightening a bolt may seem like a way to ensure a secure fit, but it can cause bolt stretching, weaken the metal, and lead to premature failure. When a bolt is torqued beyond its designed limit:
- The metal can stretch past its elastic limit, reducing its ability to hold the necessary clamping force.
- Over-tightened fasteners may snap under stress, leading to a loss of structural integrity.
- Components such as cylinder heads, main bearings, and rocker arm assemblies may become damaged due to excessive clamping force.
Following the correct torque sequence and using a calibrated torque wrench ensures that bolts are tightened within their safe range without compromising strength or durability.
2. Prevents Under-Torquing
Under-torquing a bolt or fastener can be equally problematic. When a bolt is not tightened to its specified torque:
- Vibrations can loosen bolts over time, causing key engine components to shift out of alignment.
- Oil and coolant leaks may develop if cylinder head bolts are not torqued correctly, leading to overheating and engine failure.
- A loose flywheel or crankshaft pulley can cause excessive vibrations, leading to increased wear on bearings and seals.
- Loose main bearing caps and connecting rod bolts can result in catastrophic engine damage due to misalignment and uneven load distribution.
By ensuring bolts are tightened to the exact torque specification, mechanics can prevent costly engine failures and avoid premature component wear.
3. Ensures Even Clamping Pressure

An engine is designed to operate under precise tolerances, and even clamping pressure is critical for proper sealing and mechanical stability. Uneven torque distribution can cause:
- Cylinder head gasket failure, leading to compression leaks and coolant loss.
- Warping of engine components, especially aluminum cylinder heads, which are sensitive to improper torque application.
- Bearing misalignment, resulting in excessive friction, overheating, and potential seizure of moving parts.
By following Cummins’ recommended torque specs, mechanics and technicians can ensure that cylinder heads, crankshafts, and connecting rods are properly secured. This reduces the risk of mechanical failure, enhances engine efficiency, and extends the lifespan of critical components.
4. Prevents Fastener Fatigue and Improves Serviceability
Repeated over-tightening or under-tightening of bolts can lead to fastener fatigue, making future maintenance and repairs more challenging. A bolt that has been improperly torqued multiple times:
- Loses its original elasticity, making it more prone to snapping or loosening under stress.
- Can become difficult to remove due to excessive tightening, leading to stripped threads or seized fasteners.
- May require expensive replacements if it damages the surrounding engine components.
Using proper torque techniques and tools ensures that bolts remain serviceable for future repairs, reducing overall maintenance costs and preventing downtime for marine, industrial, or trucking applications.
5. Improves Performance and Efficiency
An engine with properly torqued components runs more efficiently, as it minimizes energy loss, fluid leaks, and excess vibrations. This results in:
- Improved fuel efficiency, as all moving parts operate with minimal friction and resistance.
- Reduced wear on internal components, leading to longer service intervals and fewer breakdowns.
- Optimal compression and power output, ensuring the engine delivers consistent performance under various load conditions.
By following Cummins’ recommended torque settings, you protect your engine investment, minimize downtime, and ensure maximum reliability in demanding environments.



 Free US Calls: 1-888-433-4735
Free US Calls: 1-888-433-4735 International: 305-545-5588
International: 305-545-5588