
Introduction
The Cummins KTA38 and KTA50 are powerhouse diesel engines designed for extreme-duty applications such as marine, industrial, and power generation sectors. These engines are known for their durability and efficiency, but to ensure optimal performance, proper identification and regular maintenance are critical.
Understanding your engine’s specifications and following maintenance best practices can prevent costly repairs, minimize downtime, and extend the lifespan of these high-performance engines. This comprehensive guide will cover engine identification, maintenance schedules, and general best practices to help you keep your Cummins KTA38 and KTA50 in peak condition.
Parts Catalog for KTA38 Cummins Marine and Industrial Engines
Parts Catalog for KTA50 Cummins Marine and Industrial Engines

Identifying Your Cummins KTA38 and KTA50 Engine
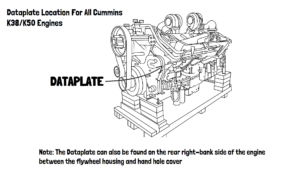
Before performing any maintenance or ordering replacement parts, it is essential to accurately identify your engine model, serial number, and CPL (Critical Parts List) number. This ensures compatibility with parts and service procedures.
Where to Find the Engine Data Plate
Every Cummins KTA38 and KTA50 engine is equipped with a data plate that provides essential identification details. This plate is typically located on the side of the engine block, near the fuel pump or the timing gear cover.
Key Information on the Data Plate

- Model Number – Specifies the exact configuration of your Cummins engine.
- Serial Number – A unique identifier assigned to each engine for tracking and service records.
- CPL (Critical Parts List) Number – Indicates the specific parts and configurations used in manufacturing the engine.
Why Engine Identification is Important
- Ensures Correct Parts Selection – Ordering the wrong parts can lead to improper fitment, reduced efficiency, and even engine
damage.
- Facilitates Proper Maintenance – Different CPL numbers may have variations in maintenance procedures, such as torque settings and filter specifications.
- Aids in Troubleshooting – Mechanics can refer to the CPL number to determine the exact specifications of components, simplifying diagnostics and repairs.
Verifying Engine Identification
To verify engine identification:
- Locate the Data Plate – Clean the plate if necessary to ensure the information is legible.
- Compare with Service Documentation – Cross-check the engine serial number with Cummins service records.
- Consult an Expert – If in doubt, contact a Cummins-certified dealer or Diesel Pro Power for assistance.
General Maintenance Guidelines for Cummins KTA38 and KTA50
Regular maintenance is essential to keeping your KTA38 and KTA50 engines running smoothly. Neglecting routine checks and servicing can lead to excessive wear, efficiency loss, and unexpected failures.
1. Lubrication and Oil Maintenance

Proper lubrication is the lifeblood of your engine. Using the right oil and maintaining the correct levels is crucial for minimizing wear and ensuring smooth operation.
Choosing the Right Lubricant
- Use Cummins-approved engine oils that meet API CI-4, CJ-4, or CK-4 specifications.
- Viscosity Grade – Typically, 15W-40 is recommended for most operating conditions.
- Synthetic vs. Conventional Oils – Synthetic oils provide better high-temperature stability and longer drain intervals.
Oil Change Intervals
- Every 250 hours or 6 months – Replace oil and oil filters to remove contaminants.
- Under heavy-duty conditions – Shorten intervals if operating in extreme temperatures or high-load environments.
Checking Oil Levels
- Park the engine on level ground and allow it to cool.
- Remove the dipstick, wipe it clean, reinsert it fully, and then check the level.
- If low, add the recommended oil type until it reaches the “Full” mark.
- Inspect for leaks around seals and gaskets.
2. Cooling System Maintenance

A properly functioning cooling system prevents overheating, which can lead to severe engine damage.
Coolant Selection
- Use Cummins-approved extended-life coolant (ELC) for optimal heat dissipation.
- Maintain a 50/50 mix of coolant and distilled water to prevent corrosion and freezing.
Cooling System Inspection
- Daily – Check coolant levels and look for leaks.
- Every 1,500 hours – Drain and flush the cooling system to remove sediment buildup.
- Inspect Radiator and Hoses – Look for cracks, leaks, or blockages that may restrict coolant flow.
- Monitor Thermostat Functionality – Ensure proper opening and closing to regulate engine temperature.
3. Fuel System Maintenance

A clean and efficient fuel system is critical for maximum power output and fuel economy.
Fuel Quality Considerations
- Use high-quality diesel fuel that meets Cummins specifications.
- Avoid fuel contamination by keeping tanks and storage areas clean.
- Drain water from fuel separators weekly to prevent injector damage.
Fuel Filter Replacement
- Primary and Secondary Filters – Replace at 250-hour intervals or sooner in dirty environments.
- Bleeding Air from the System – After filter changes, bleed air to prevent hard starting and rough operation.
4. Air Intake and Turbocharger Maintenance

The air intake system plays a crucial role in engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control.
Air Filter Maintenance
- Inspect filters weekly and replace them every 1,500 hours or as needed.
- Use only Cummins-approved filters to ensure proper filtration and airflow.
Turbocharger Inspection
- Check for excessive shaft play or oil leaks around the turbo housing.
- Listen for unusual noises that could indicate bearing failure.
- Inspect boost pressure to confirm proper operation.
5. Valve and Injector Maintenance

Valves and injectors are critical for efficient combustion and power delivery.
Valve Adjustments
- Check and adjust valve clearances every 1,500 hours to maintain proper sealing.
- Use factory-specified torque values when tightening valve adjustments.
Fuel Injector Service
- Inspect injectors for leaks and carbon buildup.
- Perform injector pop-testing to ensure correct spray patterns.
- Replace worn injectors to prevent misfiring and poor fuel economy.
6. Fasteners and Torque Specifications
Maintaining correct torque values on critical fasteners ensures engine integrity and prevents failures.
Common Torque Values
| Component | Recommended Torque (ft-lbs) |
| Cylinder Head Bolts | 125-135 |
| Main Bearing Caps | 220-240 |
| Connecting Rod Bolts | 90-110 |
| Rocker Arm Adjusting Screws | 18-22 |
Always refer to the Cummins service manual for exact torque values based on your engine’s CPL number.
Conclusion
Proper identification and maintenance of your Cummins KTA38 and KTA50 engines are essential for ensuring long-term performance, efficiency, and reliability.
By locating the engine data plate, verifying the model and CPL number, and adhering to routine maintenance schedules, operators can prevent costly repairs and maximize uptime.
Key Takeaways:
✔ Always verify engine identification before sourcing replacement parts.
✔ Follow the recommended maintenance schedule to extend engine life.
✔ Use only Cummins-approved lubricants, coolants, and filters.
✔ Monitor oil, fuel, and cooling systems to prevent breakdowns.
✔ Ensure all fasteners are torqued to factory specifications.
For high-quality aftermarket Cummins KTA38 and KTA50 parts, visit Diesel Pro Power, where we provide premium engine components to keep your equipment running at peak performance.
Parts Catalog for KTA38 Cummins Marine and Industrial Engines
Parts Catalog for KTA50 Cummins Marine and Industrial Engines



 Free US Calls: 1-888-433-4735
Free US Calls: 1-888-433-4735 International: 305-545-5588
International: 305-545-5588