The Cummins N14 engine is a powerful and reliable diesel engine widely used in heavy-duty applications. Whether you are troubleshooting, maintaining, or performing a complete rebuild, understanding its service procedures is critical. This guide provides an overview of servicing your Cummins N14 engine based on the official service manuals.
1. Introduction to the Cummins N14 Engine
The Cummins N14 is a six-cylinder, turbocharged, and aftercooled diesel engine that offers both mechanical and electronic fuel injection systems. It comes in three primary versions:
- STC (Step Timing Control) – Mechanical fuel injection with timing control for cold starts.
- CELECT™ – Electronic fuel injection with an ECM for fuel control.
- CELECT™ Plus – Advanced electronic fuel system for improved fuel efficiency and emissions control.
2. Engine Identification and Components
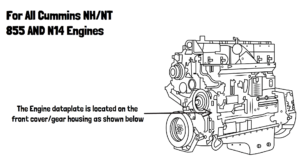
Locating the Engine Data Plate
The engine data plate is on the fuel pump side of the rocker lever housing. It contains essential information, including:
- Engine Serial Number (ESN)
- Control Parts List (CPL)
- Model and calibration codes
Key Engine Components
- Cylinder Block & Head – Houses pistons, valves, and the combustion chamber.
- Fuel System – Includes injectors, fuel lines, and pump.
- Lubrication System – Oil pump, filters, and bearings for smooth operation.
- Cooling System – Radiator, thermostat, and water pump.
- Air Intake & Exhaust System – Turbocharger, air filter, and exhaust manifold.
- Electrical System – Sensors, wiring harness, and ECM.
3. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Engine Won’t Start
- Check the battery connections and starter motor.
- Inspect fuel filters and lines for blockages or air leaks.
- Verify proper operation of the ECM (if applicable).
Excessive Smoke
- Black Smoke: Overfueling, clogged air filters, or turbocharger failure.
- White Smoke: Fuel timing issues, low compression, or coolant leakage.
- Blue Smoke: Oil burning due to worn piston rings or valve seals.
Overheating
- Low coolant levels or leaks.
- Malfunctioning thermostat or water pump.
- Clogged radiator or intercooler.
Low Oil Pressure
- Insufficient oil or worn-out oil pump.
- Blocked oil filters or galleries.
- Worn bearings causing excessive clearance.
4. Step-by-Step Service Procedures
A. Fuel System Maintenance
- Inspect and Replace Fuel Filters
- Use Fleetguard FS1000 or equivalent fuel-water separator.
- Fill new filters with clean fuel before installation.
- Checking Injectors
- CELECT™ injectors require special calibration tools.
- Check for air in the fuel lines using a sight glass.
- Fuel Pump Testing
- Measure fuel inlet restriction using a manometer.
- Inspect the fuel drain line restriction (should not exceed 3.5 inHg).
B. Lubrication System Maintenance
- Oil Change Interval
- Replace oil every 15,000 miles or 500 hours.
- Use 15W-40 heavy-duty diesel oil meeting Cummins CES 20078 specs.
- Oil Filter Replacement
- Spin-on type filters should be replaced with OEM-quality filters.
- Tighten filters ½ to ¾ turns past gasket contact.
- Checking Oil Pressure
- Use a pressure gauge at the main rifle to verify correct oil pressure.
- Normal range: 30–45 psi at high idle.
C. Cooling System Maintenance
- Radiator & Coolant Checks
- Use a 50/50 coolant mixture with Cummins-approved SCA additives.
- Inspect for leaks and flush the system every 2 years.
- Water Pump Inspection
- Check for leaks or bearing play.
- Replace if coolant is leaking from the weep hole.
- Thermostat Replacement
- The thermostat should open at 180°F to 195°F.
- Use OEM-recommended thermostat for optimal engine performance.
D. Air Intake & Exhaust System
- Turbocharger Inspection
- Check for excessive shaft play or oil leaks.
- Verify proper boost pressure using a manifold pressure gauge.
- Air Filter Maintenance
- Replace filters every 25,000 miles or once per year.
- Inspect for clogging or collapsed intake hoses.
- Exhaust Manifold Check
- Inspect for cracks or carbon buildup.
- Ensure turbo mounting bolts are properly torqued.
E. Electrical System & ECM Diagnostics
- Battery & Alternator Checks
- Ensure 14V-14.5V charging at idle.
- Check battery terminals for corrosion.
- Sensor Testing
- Verify coolant temperature, oil pressure, and intake air sensors.
- Use Cummins Insite™ software for electronic diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- ECM Reset & Calibration
- Resetting ECM can clear minor electronic glitches.
- Reprogram ECM if new injectors are installed.
5. Step-by-Step Engine Rebuild Process
If your Cummins N14 requires a full rebuild, follow these steps:
A. Disassembly
- Drain all fluids and remove external components.
- Remove cylinder head, pistons, and camshaft.
- Inspect the crankshaft and bearings for wear.
B. Cleaning & Inspection
- Steam clean the block and head.
- Check for cracks or warping using a straight edge.
- Inspect liners, rings, and connecting rods.
C. Reassembly & Torque Specs
- Install new pistons, rings, and bearings (OEM-spec).
- Torque main caps: 30 ft-lb + 90° turn.
- Adjust valve lash:
- Intake: 0.014 inches
- Exhaust: 0.027 inches
- Install fuel injectors and prime lubrication system before startup.
6. Safety Precautions When Servicing the N14
- Always disconnect the battery before working on the electrical system.
- Use proper lifting tools when handling heavy components.
- Wear eye protection when working around pressurized fuel and coolant lines.
- Never exceed torque specifications, as overtightening can cause component failure.
Conclusion
The Cummins N14 is a robust engine that can last over a million miles with proper maintenance. Regular inspections, oil changes, and timely replacements of key components ensure its reliability. Whether you’re performing routine servicing or a full engine rebuild, following this guide will help you keep your N14 running smoothly.
For more Cummins N14 parts, visit Diesel Pro Power.
Why Mechanics, Fleet Managers, and Fleet Owners Choose Diesel Pro Power for Cummins N14 Parts
1. Cummins N14–Specific Engine Knowledge
The Cummins N14 is a legendary heavy-duty diesel engine known for durability in on-highway, industrial, and vocational applications. Diesel Pro Power understands the variations within the N14 platform, including Celect and Celect Plus configurations, and supplies parts correctly matched to each engine setup.
2. Premium Aftermarket Parts Built for High-Mileage Engines
Diesel Pro Power offers premium aftermarket N14 components engineered to withstand high mileage, continuous loads, and demanding operating conditions. These parts are selected to support reliable performance and long service intervals in fleet environments.
3. Accurate Fitment That Reduces Downtime
Incorrect parts create costly delays. Diesel Pro Power focuses on accurate part identification and fitment verification, helping customers avoid ordering mistakes, rework, and unnecessary downtime during maintenance or overhaul.
4. Trusted by 40,000+ Customers Worldwide
With more than 40,000 customers across 180+ countries, Diesel Pro Power is a proven supplier for professionals maintaining Cummins N14 engines worldwide.
5. 4.9-Star Google Rating for Service & Support
A 4.9 Google rating reflects Diesel Pro Power’s reputation for quality parts, responsive service, and knowledgeable technical support—critical for fleets managing uptime and operating costs.
6. Long-Term Value for Fleet Operations
Quality parts help extend engine life and protect capital investments. Diesel Pro Power’s Cummins N14 parts support dependable operation, reduced repeat failures, and predictable maintenance planning.



 Free US Calls: 1-888-433-4735
Free US Calls: 1-888-433-4735 International: 305-545-5588
International: 305-545-5588