Introduction to the Cummins N14 Engine

The Cummins N14 is a six-cylinder, turbocharged, and aftercooled diesel engine widely known for its reliability and durability in trucking, industrial, and marine applications. This powerhouse features both mechanical and electronic fuel injection systems, offering versatility and performance optimization across various operating conditions.
Parts Catalog for N14 Cummins Industrial Engines
It comes in three primary versions:
- STC (Step Timing Control): A mechanical fuel injection system incorporating step timing control for better cold start performance.
- CELECT™: An electronically controlled fuel injection system using an ECM (Engine Control Module) for precise fuel control.
- CELECT™ Plus: An advanced electronic fuel injection system designed to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
With a displacement of 14 liters (855 cubic inches), the Cummins N14 is one of the most powerful engines in its class. It has been a popular choice for heavy-duty applications, including long-haul trucking, construction equipment, and marine vessels.
Cummins N14 Engine Specifications
The Cummins N14 engine features robust engineering and specifications tailored for efficiency, performance, and longevity.
General Specifications
- Configuration: Inline 6-cylinder
- Displacement: 14.0 liters (855 cubic inches)
- Bore and Stroke: 5.50 inches x 6.00 inches (140mm x 152mm)
- Aspiration: Turbocharged and Aftercooled
- Compression Ratio: 14.0:1 to 16.0:1 (varies by model)
- Horsepower Range: 310 – 525 HP
- Torque: 1250 – 1850 lb-ft
- Fuel System: PT (Pressure-Time) or Electronic (CELECT™, CELECT™ Plus)
- Cooling System: Liquid-cooled with thermostatic regulation
Engine Variants
- N14 STC: Uses Step Timing Control to adjust fuel injection timing based on load and temperature.
- N14 CELECT™: Introduced an electronic fuel control system to enhance fuel efficiency and emissions.
- N14 CELECT™ Plus: An upgraded version with improved ECM programming, injector control, and diagnostics.
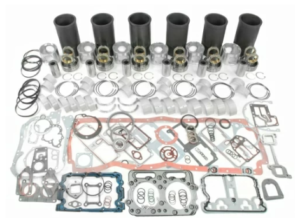
Rebuild Kit & Related Components for Cummins N14 Industrial Engine
Key Components and Operation
Cylinder Block and Head

The N14 cylinder block is a cast-iron structure, providing rigidity and heat dissipation. It houses:
- Cylinders and pistons
- Main bearings and crankshaft
- Lubricating oil and cooling passages
The cylinder head incorporates valve seats, intake/exhaust ports, and fuel injectors, making it critical for combustion efficiency.
Cylinder Head & Related Components for Cummins N14 Industrial Engine
Fuel System (PT and Electronic Injection)

The Cummins N14 fuel system varies by model:
PT Fuel System (STC Models)
- Uses a mechanical PT (Pressure-Time) fuel system, relying on fuel pressure and injection timing for fuel delivery.
- Step Timing Control (STC) adjusts injection timing to improve cold starts and efficiency at low loads.
Electronic Fuel Injection (CELECT™ and CELECT™ Plus)
- Uses Electronic Control Modules (ECM) to regulate fuel delivery with electronic unit injectors.
- CELECT™ Plus improved fuel mapping, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
Injector & Related Components for Cummins N14 Industrial Engine
Turbocharging and Aftercooling

The N14 turbocharger provides increased airflow, optimizing combustion efficiency and power output.
- The aftercooler reduces intake air temperature, increasing air density for better performance.
- Turbocharging helps maintain power output at high altitudes and under load.
Turbocharger & Related Components for Cummins N14 Industrial Engine
Lubrication System
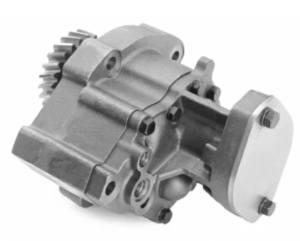
The lubrication system ensures all moving parts are protected against wear:
- Oil Pump: Circulates oil through the engine.
- Oil Filters: Remove contaminants.
- Piston Cooling Nozzles: Spray oil to cool the piston crowns.
Lubrication System & Related Components for Cummins N14 Industrial Engine
Cooling System

- Water Pump: Circulates coolant.
- Radiator: Removes excess heat.
- Thermostat: Regulates coolant flow.
- Oil Cooler: Maintains engine oil temperature.
Cooling System & Related Components for Cummins N14 Industrial Engine
Maintenance and Service Intervals
Proper maintenance ensures maximum performance and longevity of the Cummins N14 engine.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
| Service Interval | Maintenance Task |
| Daily | Check oil level, coolant level, fuel leaks. |
| Every 15,000 miles (24,000 km) | Change oil and oil filter. |
| Every 30,000 miles (48,000 km) | Inspect fuel filters, check turbocharger. |
| Every 60,000 miles (96,000 km) | Valve adjustment, inspect injectors, clean cooling system. |
| Every 120,000 miles (192,000 km) | Overhaul fuel injectors, replace thermostat. |
| Every 300,000 miles (480,000 km) | Full engine inspection, replace bearings if necessary. |
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
1. Low Power Output
- Potential Causes:
- Clogged air filter
- Malfunctioning fuel injectors
- Turbocharger failure
- Excessive fuel line restriction
- Solution:
- Replace air filter.
- Check injectors and turbo for wear.
- Inspect fuel pressure.
2. Excessive Fuel Consumption
- Potential Causes:
- Faulty ECM tuning (CELECT™)
- Leaking injectors
- Air-fuel ratio imbalance
- Solution:
- Recalibrate ECM.
- Inspect injectors for leaks.
- Ensure turbocharger is functioning correctly.
3. Hard Starting / No Start
- Potential Causes:
- Fuel system air leak
- Weak battery or faulty starter
- Incorrect timing
- Solution:
- Check for fuel leaks.
- Test battery voltage.
- Verify fuel pump pressure.
4. White Smoke (Cold Start Issues)
- Potential Causes:
- Low compression in cylinders
- Faulty injectors
- Excessive fuel timing retard
- Solution:
- Perform a compression test.
- Inspect injectors for carbon build-up.
- Adjust timing.
5. Black Smoke (Overfueling or Poor Air Supply)
- Potential Causes:
- Clogged air filter
- Sticking injectors
- Turbocharger failure
- Solution:
- Replace the air filter.
- Clean or replace injectors.
- Inspect turbo and boost pressure.
Performance Upgrades for the Cummins N14
Many Cummins N14 owners seek performance upgrades for better power and fuel economy.
ECM Tuning (CELECT™ and CELECT™ Plus Models)
- A custom ECM tune can optimize fuel injection timing and boost efficiency.
Turbocharger Upgrade
- Installing a high-performance turbo can increase airflow and power output.
High-Flow Air Filters
- A less restrictive air intake improves fuel efficiency and acceleration.
Exhaust System Improvements
- A performance exhaust reduces backpressure, increasing horsepower.
Conclusion
The Cummins N14 engine remains one of the most reliable diesel engines for heavy-duty applications. Whether you’re maintaining an STC, CELECT™, or CELECT™ Plus model, regular maintenance, troubleshooting, and performance tuning are key to keeping this engine running efficiently.
For more advanced repairs, always consult a Cummins-certified technician to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Parts Catalog for N14 Cummins Industrial Engines



 Free US Calls: 1-888-433-4735
Free US Calls: 1-888-433-4735 International: 305-545-5588
International: 305-545-5588