Introduction
Proper maintenance of the Cummins N14 engine is essential for ensuring its longevity, reliability, and optimal performance. This guide provides detailed step-by-step service procedures for key engine systems, including the fuel system, lubrication system, cooling system, air intake & exhaust, electrical system, and ECM diagnostics. Additionally, we cover common troubleshooting methods to help diagnose issues related to performance, emissions, and mechanical wear.
Parts Catalog for N14 Cummins Industrial Engines
A. Fuel System Maintenance

The fuel system plays a critical role in the engine’s efficiency and performance. Proper maintenance ensures optimal fuel delivery, combustion, and injector operation.
1. Inspect and Replace Fuel Filters

Recommended Fuel Filters:
- Use Fleetguard FS1000 or an equivalent fuel-water separator.
- Ensure filters meet Cummins fuel system specifications to prevent contamination.
Step-by-Step Fuel Filter Replacement Procedure:
- Turn off the engine and allow it to cool.
- Locate the primary and secondary fuel filters. The primary filter is typically the fuel-water separator, while the secondary filter is mounted on the engine.
- Drain fuel from the old filter using the provided drain plug.
- Remove the old fuel filter using a strap wrench.
- Pre-fill the new filter with clean diesel fuel to minimize air introduction.
- Lubricate the new filter gasket with a thin coat of diesel fuel.
- Install the new filter by tightening ½ to ¾ turns past gasket contact (do not overtighten).
- Prime the fuel system using the manual fuel pump or turning the key to “ON” without cranking (for CELECT™ engines).
- Start the engine and check for leaks.
2. Checking Injectors

Signs of Faulty Injectors:
- Rough idle or misfires
- Excessive black smoke
- Loss of power and fuel efficiency
Steps to Inspect Injectors on a CELECT™ System:
- Use Cummins Insite™ software to monitor individual injector performance.
- Perform a cylinder balance test by disabling injectors one at a time and observing RPM drops.
- Check fuel pressure at the rail using a sight glass to detect air bubbles (air in fuel lines can cause injector misfires).
- If injectors fail tests, replace with Cummins-approved replacements and recalibrate ECM.
3. Fuel Pump Testing
Fuel Pump Inspection Steps:
- Check fuel inlet restriction using a manometer (should not exceed 6 inHg under full load).
- Inspect fuel drain line restriction (should be under 3.5 inHg).
- Measure fuel pressure at idle and at full throttle (ideal pressure is 25-35 psi).
- If readings are low, inspect fuel lines, pressure regulator, and fuel pump seals for leaks.
Fuel Filter & Related Components for Cummins N14 Industrial Engine
B. Lubrication System Maintenance
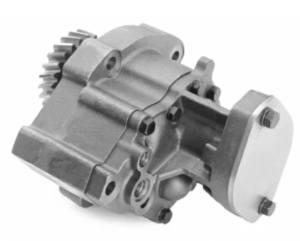
The lubrication system is responsible for reducing friction, cooling engine parts, and preventing wear.
1. Oil Change Interval
- Replace oil every 15,000 miles or 500 hours, whichever comes first.
- Use 15W-40 heavy-duty diesel oil meeting Cummins CES 20078 specifications.
- Inspect oil levels daily to ensure proper lubrication.
2. Oil Filter Replacement
Oil Filter Replacement Steps:
- Drain engine oil while the engine is warm for better flow.
- Remove the oil filter using a filter wrench.
- Apply a thin layer of oil to the new filter gasket.
- Install the new filter by tightening ½ to ¾ turns past gasket contact.
- Refill oil to proper levels and check for leaks.
3. Checking Oil Pressure
Oil Pressure Specifications:
- 30–45 psi at high idle
- 10–15 psi at low idle
Steps to Verify Oil Pressure:
- Install a mechanical oil pressure gauge at the main oil rifle.
- Start the engine and let it warm up.
- Compare readings with standard oil pressure ranges.
- If oil pressure is low, inspect oil pump, bearings, and pressure relief valve.
Lubrication System & Related Components for Cummins N14 Industrial Engine
C. Cooling System Maintenance

The cooling system regulates engine temperature to prevent overheating and ensure efficient operation.
1. Radiator & Coolant Checks
Coolant Maintenance Steps:
- Use a 50/50 coolant mixture with Cummins-approved SCA additives.
- Inspect radiator hoses for leaks, cracks, or loose clamps.
- Flush the cooling system every 2 years to remove scale buildup.
Cooling System & Related Components for Cummins N14 Industrial Engine
2. Water Pump Inspection
Signs of a Failing Water Pump:
- Coolant leaks from the weep hole
- Overheating under load
- Squeaking or grinding noises
To inspect:
- Check the water pump bearing for play by manually moving the pulley.
- If coolant is leaking from the weep hole, replace the pump.
3. Thermostat Replacement

Thermostat Specifications:
- Opens at 180°F to 195°F
Replacement Procedure:
- Drain coolant from the system.
- Remove the thermostat housing and old thermostat.
- Install a new Cummins-recommended thermostat.
- Refill the coolant and purge air from the system.
Thermostat & Related Components for Cummins N14 Industrial Engine
D. Air Intake & Exhaust System

1. Turbocharger Inspection
Check for Turbo Issues:
- Excessive shaft play
- Oil leaks into the compressor housing
- Loss of boost pressure
Use a manifold pressure gauge to verify proper boost levels (25-30 psi under load).
2. Air Filter Maintenance
- Replace air filters every 25,000 miles or annually.
- Check for collapsed intake hoses restricting airflow.
3. Exhaust Manifold Check
- Inspect for cracks, leaks, or excessive carbon buildup.
- Ensure turbo mounting bolts are properly torqued.
Turbocharger & Related Components for Cummins N14 Industrial Engine
E. Electrical System & ECM Diagnostics

1. Battery & Alternator Checks
- Ensure charging voltage is 14V-14.5V at idle.
- Inspect battery terminals for corrosion.
2. Sensor Testing
- Use Cummins Insite™ to verify coolant temp, oil pressure, and intake air sensors.
3. ECM Reset & Calibration
- Resetting ECM clears minor glitches.
- Reprogram ECM if new injectors are installed.
Starter & Related Components for Cummins N14 Industrial Engine
F. Engine Testing & Troubleshooting

1. How to Perform an Engine Compression Test
- Remove all injectors.
- Insert a compression gauge into each cylinder.
- Crank the engine and record readings (400-500 psi is normal).
2. Common Causes of Excessive Blowby
- Worn piston rings
- Glazed cylinder liners
- Cracked pistons
3. Checking Crankshaft End Play

- Use a dial indicator on the crankshaft flange.
- Normal clearance: 0.003-0.015 inches.
4. Troubleshooting Excessive White Smoke
- Check for coolant leaks or low compression.
- Inspect injector spray patterns.
5. Cold Weather Start-Up Procedure
- Use a block heater.
- Allow engine to idle at 1000 RPM before applying load.
Conclusion
Proper step-by-step maintenance of the Cummins N14 engine ensures long service life, reliability, and optimal performance. By following these detailed service procedures, you can minimize downtime, prevent costly repairs, and maintain engine efficiency.
Parts Catalog for N14 Cummins Industrial Engines



 Free US Calls: 1-888-433-4735
Free US Calls: 1-888-433-4735 International: 305-545-5588
International: 305-545-5588
I will know, I thank for the information.