
The electrical and exhaust systems of the Detroit Diesel 6V71, 8V71, 12V71, and 16V71 engines play critical roles in ensuring the efficient starting, operation, and exhaust gas management of these engines. This guide explores the electrical components, including starting motors, alternators, and protective systems, as well as the maintenance and troubleshooting of exhaust manifolds and turbochargers. Additionally, procedures for inspecting and replacing fuse plugs and other protective elements are detailed for effective system management.
Overview of Electrical Components in 6V71, 8V71, 12V71, and 16V71 Engines
The electrical system is integral to starting, monitoring, and protecting the engine. Key components include:
1. Starting Motors for Detroit Diesel Engine V71 Engines

Function:

The starter motor converts electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy, delivering the torque necessary to crank and start the Detroit Diesel V71 engine. It engages the flywheel, turning the crankshaft to initiate combustion.
Design:

- Heavy-Duty Motor: Built to handle the high torque required for starting large diesel engines, ensuring durability under extreme conditions.
- Gear-Driven System: Ensures efficient energy transfer to the engine’s flywheel for reliable starts.
- Solenoid Engagement: The integrated solenoid ensures smooth and precise engagement with the flywheel, minimizing wear.
- Corrosion-Resistant Housing: Sealed against moisture and debris for longer service life.
- Thermal Protection: Prevents overheating during extended operation.
Inspection:

- Electrical Connections: Inspect terminals and cables for corrosion, loose fittings, or frayed wires. Clean with a wire brush and apply dielectric grease. Tighten all connections.
- Motor Housing & Components: Check for cracks, dents, or damage. Ensure mounting bolts are secure and inspect the pinion gear for worn teeth.
- Solenoid Function: Listen for the click during ignition. If absent, inspect or replace the solenoid.
- Brush & Commutator: Disassemble to inspect brushes for wear and clean the commutator with fine-grit sandpaper if necessary.
- Drive Mechanism: Ensure the pinion gear moves smoothly along the shaft and engages properly.
Maintenance:

- Clean & Tighten: Regularly clean and tighten battery and starter terminals to prevent voltage drops.
- Lubrication: Lightly grease the shaft and pinion gear with high-temperature grease. Avoid over-lubrication.
- Test Efficiency: Conduct voltage drop tests and replace cables if power loss is detected.
- Replace Worn Parts: Check and replace worn brushes, bearings, or damaged solenoids.
- Preventive Care: Inspect for oil leaks that could contaminate the starter, and verify the engine’s ground connections.
Starter & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 6V71 Non- Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Starter & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 6V71 Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Starter & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 8V71 Non- Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Starter & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 8V71 Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Starter & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 12V71 Non- Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Starter & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 12V71 Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Starter & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 16V71 Non- Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Starter & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 16V71 Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
2. Alternators For Detroit Diesel V71 Series Engines

Function:

Alternators are critical components in Detroit Diesel engines, responsible for generating the electrical power necessary to:
- Recharge the Battery: Ensures the battery remains fully charged, providing reliable starts and supporting electrical systems.
- Power Electrical Systems: Supplies consistent energy to vital engine components, including the ignition system, lights, instrumentation, and control units. This ensures continuous operation of essential functions while the engine is running.
Design:

- Belt-Driven Mechanism: Alternators are powered by a belt connected to the engine’s crankshaft. This design allows the alternator to generate electricity proportionally to the engine’s speed.
- Voltage Regulator: Integrated voltage regulators maintain consistent electrical output, protecting the battery and electrical systems from voltage fluctuations and ensuring efficient charging.
- Cooling Features: Many alternators include internal fans that provide necessary cooling to prevent overheating during operation.
- Sealed or Serviceable Bearings: Modern alternators often have sealed bearings for maintenance-free operation, while older designs may require periodic lubrication.
- Durable Housing: Designed to withstand vibrations, dirt, and moisture in harsh engine environments.
Inspection:

Regular inspections are essential to maintain alternator performance and avoid electrical issues:
- Belt Condition and Tension: Inspect the drive belt for wear, cracks, or fraying. Ensure proper tension—neither too loose nor too tight—to avoid slippage and ensure efficient power transfer.
- Electrical Connections: Check all terminals and wiring for signs of corrosion, damage, or looseness. Tighten and clean connections as necessary.
- Voltage Output Testing: Use a multimeter to test the voltage output while the engine is running. A healthy alternator should produce between 13.5 to 14.5 volts. Readings outside this range may indicate faulty components.
- Auditory Inspection: Listen for unusual sounds such as grinding, whining, or knocking, which may indicate bearing wear or internal damage.
- Visual Check: Inspect the alternator’s housing for signs of overheating (like discoloration) or physical damage.
Maintenance:

Proper maintenance ensures the longevity and efficiency of the alternator:
- Replace Worn Belts: Promptly replace belts that show wear, cracks, or signs of slipping. Ensure proper tension after installation.
- Clean Electrical Terminals: Remove dirt and corrosion from terminals to ensure efficient electrical flow. Apply dielectric grease to prevent future corrosion.
- Lubricate Bearings (If Required): If the alternator features serviceable bearings, lubricate them according to manufacturer specifications. For sealed bearings, periodic inspection is sufficient.
- Check and Tighten Mounting Hardware: Ensure all bolts and brackets are secure to avoid vibrations and misalignment.
- Inspect Cooling Components: Clean cooling vents to ensure proper airflow and prevent overheating.
- Regular Voltage Testing: Conduct periodic voltage output checks to ensure the alternator remains within the optimal range.
3. Protective Systems
- Components:
- Circuit breakers and fuses protect the electrical system from overloading or short circuits.
- Sensors monitor oil pressure, coolant temperature, and other critical parameters, triggering alarms or shutdowns to prevent damage.
- Inspection:
- Test sensors periodically to ensure accurate readings.
- Inspect fuses and circuit breakers for signs of wear or damage.
- Maintenance:
- Replace faulty sensors or damaged fuses immediately to maintain system integrity.
- Test alarms and shutdown systems regularly.
Alternator & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 6V71 Non- Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Alternator & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 6V71 Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Alternator & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 8V71 Non- Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Alternator & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 8V71 Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Alternator & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 12V71 Non- Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Alternator & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 12V71 Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Alternator & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 16V71 Non- Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Alternator & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 16V71 Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Maintenance of Exhaust Manifolds and Turbochargers in 6V71, 8V71, 12V71, and 16V71 Engines
Proper maintenance of the exhaust system is essential for efficient exhaust gas removal, optimal engine performance, and prolonged engine life. In Detroit Diesel engines, the exhaust system includes the exhaust manifolds and turbochargers (if applicable). Both components must be routinely inspected and maintained to prevent performance issues, overheating, or mechanical failure.
1. Exhaust Manifolds for Detroit Diesel V71 Series Engines
Function:

The exhaust manifold is responsible for collecting exhaust gases from each cylinder and directing them into the exhaust pipe or the turbocharger. A properly functioning manifold ensures smooth gas flow, reducing backpressure and preventing heat buildup that could damage engine components.
Inspection:

Regular inspections can prevent severe damage and maintain system efficiency. Key points to check include:
- Cracks and Corrosion: Inspect the entire manifold surface for visible cracks, warping, or corrosion. Cracks can cause exhaust leaks, reduced performance, and overheating. Rust and corrosion, especially in high-moisture environments, can weaken the structure over time.
- Signs of Exhaust Leakage: Look for soot marks or discoloration around the gasket areas and mounting surfaces, which can indicate leakage.
- Gasket Condition: Examine gaskets for wear, cracks, or burning. Worn gaskets can lead to gas leaks, resulting in poor engine performance and potential damage to nearby components.
- Mounting Bolts and Studs: Check for tightness and integrity. Loose bolts can lead to exhaust leaks, while corroded or damaged studs may result in improper manifold alignment.
- Manifold Alignment: Ensure the manifold is correctly aligned with the cylinder head. Misalignment can cause gasket failure and leaks.
Maintenance:

Proper maintenance practices are essential to keep the exhaust manifold operating efficiently:
- Replace Cracked or Corroded Manifolds: If the manifold exhibits severe corrosion or cracks, it must be replaced. Attempting to repair extensively damaged manifolds is not advisable due to the high temperatures and pressures they endure.
- Install New Gaskets During Reassembly: Always use new gaskets when reinstalling the manifold to ensure a proper seal. Old or damaged gaskets will likely result in leaks.
- Torque Bolts to Manufacturer’s Specifications: Using a torque wrench, tighten all mounting bolts to the manufacturer’s recommended torque values to prevent warping or uneven sealing.
- Check for Warping: If the manifold appears warped, it should be machined or replaced to ensure a proper fit and seal.
- Clean Mounting Surfaces: Before installation, ensure all mounting surfaces are clean and free of debris, old gasket material, and corrosion to ensure a proper seal.
- Inspect Heat Shields (if applicable): If your engine is equipped with heat shields, inspect them for damage or wear. Heat shields protect nearby components from excessive heat and should be replaced if compromised.
- Monitor for Noise or Smell: If you notice unusual noises, such as ticking, or smell exhaust fumes in the engine bay, inspect the manifold immediately for potential leaks.
2. Turbochargers (If Applicable) For Detroit Deisel V71 Engines
Function:

Turbochargers significantly enhance engine performance by forcing additional air into the combustion chamber, allowing more fuel to burn efficiently. This results in increased power output, better fuel economy, and improved overall engine efficiency.
Inspection:

Routine inspection helps to ensure consistent turbocharger performance and early detection of potential issues:
- Shaft Play: Check the turbocharger shaft for excessive axial (in and out) or radial (side to side) play. Some minimal movement is acceptable, but excessive play indicates worn bearings, which can lead to turbo failure.
- Compressor and Turbine Blades: Inspect the blades for chips, cracks, or deformation. Damage can disrupt airflow and reduce turbo efficiency, potentially causing catastrophic failure if left unaddressed.
- Oil Leaks: Examine the turbocharger housing, seals, and connecting pipes for any signs of oil leakage. Oil leaks can indicate worn seals, over-pressurized oil systems, or clogged return lines.
- Foreign Object Damage: Check for debris that may have entered the compressor or turbine housing. Any foreign object damage can severely impact turbocharger performance and lifespan.
- Mounting Integrity: Ensure the turbocharger is securely mounted and that there are no loose bolts or misaligned components.
- Noise and Vibration: Listen for unusual noises such as whining, grinding, or rattling, which could indicate internal damage or imbalance.
Maintenance:

Consistent maintenance ensures the longevity and efficient performance of turbochargers:
- Clean Regularly: Periodically remove carbon deposits and soot from the compressor and turbine housing. Keeping these areas clean prevents airflow obstruction and enhances turbo performance.
- Lubrication System Check: Ensure that the turbocharger receives consistent lubrication by inspecting the oil supply and return lines. Replace clogged or damaged lines to prevent oil starvation, which can destroy the turbocharger.
- Oil Quality and Levels: Maintain proper oil levels and ensure the oil used meets the manufacturer’s specifications. Poor-quality or contaminated oil can accelerate wear and lead to failure.
- Seal Replacement: If oil leaks are detected, inspect and replace damaged seals promptly to prevent further damage and maintain optimal performance.
- Blade Repair or Replacement: Replace any damaged or worn compressor or turbine blades. Neglecting blade condition can lead to imbalances, noise, and catastrophic failure.
- Coolant System Check (if water-cooled): Ensure the coolant system is properly functioning to prevent overheating. Check for any leaks, and flush the system as needed.
- Avoid Sudden Shutdowns: Allow the engine to idle for a few minutes after heavy use. This helps cool the turbocharger and prevents oil coking, which can damage internal components.
- Inspect Air Filters: Ensure air filters are clean and properly installed to prevent debris from entering the turbocharger.
Turbo & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 6V71 Marine & Industrial Engines
Turbo & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 8V71 Marine & Industrial Engines
Turbo & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 12V71 Marine & Industrial Engines
Turbo & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 16V71 Marine & Industrial Engines
Procedures for Inspecting and Replacing Fuse Plugs and Other Protective Elements
Fuse plugs and other protective elements are essential for preventing catastrophic engine damage during abnormal operating conditions.
1. Fuse Plugs For Detroit Diesel V71 Engines
- Function:

Head Plug Kit for Detroit Diesel 6V71
Heat-sensitive fuse plugs are installed in the cylinder head to provide early warning of overheating. The plug insert melts at critical temperatures (typically 257°F or 125°C), indicating that the engine may have overheated.
- Inspection:

Head Plug Kit for Detroit Diesel Engine 12V71
- Inspect fuse plugs during routine maintenance or whenever overheating is suspected.
- Look for melted inserts, which indicate a previous overheating event.
- Replacement:

Head plug kit for Detroit Diesel engine 16V71
- If a fuse plug is melted, remove it using a suitable socket or wrench.
- Clean the installation hole and apply a high-temperature sealant to the threads of the new plug.
- Torque the replacement fuse plug to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Fuel Plugs & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 6V71 Non- Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Fuel Plugs & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 6V71 Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Fuel Plugs & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 8V71 Non- Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Fuel Plugs & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 8V71 Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Fuel Plugs & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 12V71 Non- Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Fuel Plugs & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 12V71 Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Fuel Plugs & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 16V71 Non- Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
Fuel Plugs & Related Components for Detroit Diesel 16V71 Turbo Marine & Industrial Engines
2. Pressure Relief Valves For Detroit Diesel V71 Engines
- Function:

Oil relief valve for Detroit Diesel 12V71
These valves protect the cooling and lubrication systems by releasing pressure during abnormal operating conditions.
- Inspection:

Oil Regulator Valve for Detroit Diesel 16V71 and 12V71
- Verify that valves open and close properly under pressure.
- Inspect for leaks or corrosion.
- Maintenance:

Oil Relief Valve for Detroit Diesel 6V71
- Replace valves that fail pressure tests.
- Clean or replace seals and springs as needed.
3. Thermal Sensors and Alarms For Detroit Diesel V71 Engines
- Function:

Engine oil pressure gauge with alarm system

Relay 12 volts for switch gauge
These sensors monitor engine temperature and trigger alarms or shutdowns when critical thresholds are exceeded.
- Inspection:

6 ft Engine water temperature gauge mechanical with alarm switch

24 Volt Relay For Switch Gauge
- Test sensor accuracy using a multimeter and compare readings to specifications.
- Check wiring for damage or loose connections.
- Maintenance:

Pressure Alarm System Siren 6 to 28 VDC -SAH
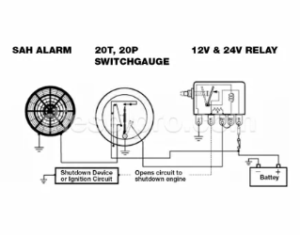
Pressure Alarm System Siren 6 to 28 VDC -SAH
- Replace faulty sensors or damaged wiring.
- Calibrate the system regularly to ensure accurate readings.
Mechanical Gauges with Alarm for Detroit Diesel V71 Marine & Industrial Engines
Mechanical Gauges for Detroit Diesel V71 Marine & Industrial Engines
12 Volt Electronic Gauges for Detroit Diesel V71 Marine & Industrial Engines
24V Electrical Gauges for Detroit Diesel V71 Marine & Industrial Engines
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
The following issues may arise in the electrical and exhaust systems of Detroit Diesel engines. Use these troubleshooting tips to resolve them:
1. Electrical System Failures For Detroit Diesel V71 Engines
- Symptoms:
Engine fails to start, battery drains quickly, or sensors provide erratic readings.
- Causes:
- Weak or dead battery.
- Faulty alternator or voltage regulator.
- Damaged wiring or connections.
- Solutions:
- Recharge or replace the battery and ensure proper terminal connections.
- Test and replace the alternator or regulator if output is insufficient.
- Repair or replace damaged wiring and tighten connections.
2. Exhaust Gas Leaks For Detroit Diesel V71 Engines
- Symptoms:
Visible smoke near the manifold, reduced engine performance, or unusual noise.
- Causes:
- Cracked exhaust manifold or worn gaskets.
- Cracked exhaust manifold or worn gaskets.
- Solutions:
- Replace damaged manifolds and install new gaskets.
- Tighten bolts to prevent leaks.
3. Turbocharger Performance Issues For Detroit Diesel V71 Engines

- Symptoms:
Loss of power, excessive exhaust smoke, or unusual whining noise.
- Causes:
- Damaged turbine blades or worn seals.
- Insufficient lubrication or cooling.
- Solutions:
- Replace damaged components and ensure proper lubrication.
- Check for blockages in oil or coolant lines.
Best Practices for Electrical and Exhaust Systems in 6V71, 8V71, 12V71, and 16V71 Engines
- Regular Inspections:
- Conduct visual inspections of electrical and exhaust components during routine maintenance.
- Test protective systems to ensure reliability.
- Replace Aging Components:
- Replace old or worn parts, such as fuse plugs, wiring, and gaskets, to avoid unexpected failures.
- Replace old or worn parts, such as fuse plugs, wiring, and gaskets, to avoid unexpected failures.
- Monitor Engine Conditions:
- Pay attention to sensor alarms and exhaust smoke patterns for early signs of trouble.
- Pay attention to sensor alarms and exhaust smoke patterns for early signs of trouble.
- Use Quality Replacement Parts:
- Always use manufacturer-recommended parts for optimal compatibility and performance.
Parts Catalog for 6V71 Non – Turbo Detroit Diesel Marine & Industrial Engine
Parts Catalog for 6V71 Turbo Detroit Diesel Marine & Industrial EnginesParts Catalog for 8V71 Non – Turbo Detroit Diesel Marine & Industrial Engine
Parts Catalog for 8V71 Turbo Detroit Diesel Marine & Industrial EnginesParts Catalog for 12V71 Non – Turbo Detroit Diesel Marine & Industrial Engine
Parts Catalog for 12V71 Turbo Detroit Diesel Marine & Industrial EnginesParts Catalog for 16V71 Non – Turbo Detroit Diesel Marine & Industrial Engine
Parts Catalog for 16V71 Turbo Detroit Diesel Marine & Industrial Engines
- Always use manufacturer-recommended parts for optimal compatibility and performance.



 Free US Calls: 1-888-433-4735
Free US Calls: 1-888-433-4735 International: 305-545-5588
International: 305-545-5588